Create a BIP! Services account
Click the "Login" button in the top-right of the BIP! Services website.
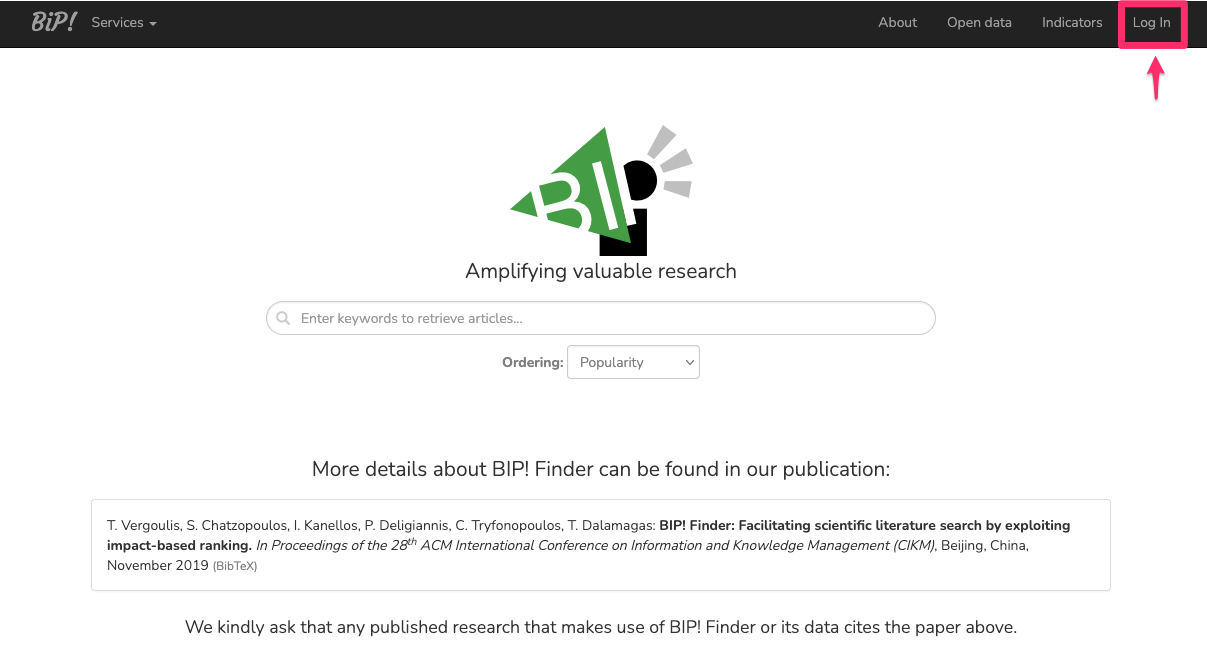
Click the "Sign up" option that exists in the Login page.
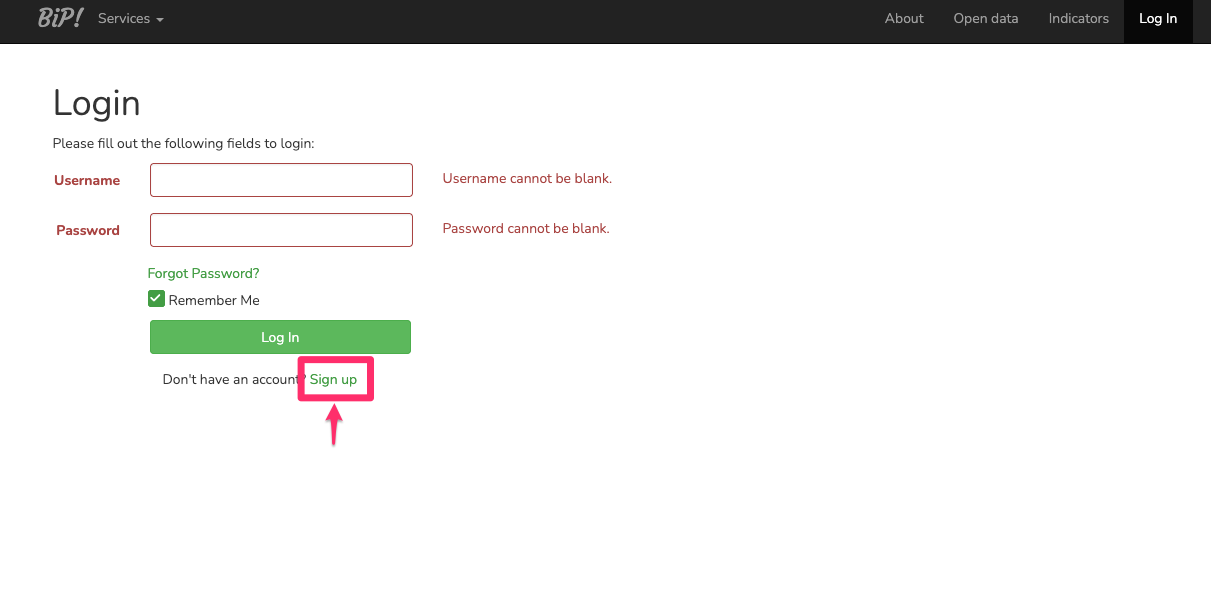
Fill out the required fields in the form.
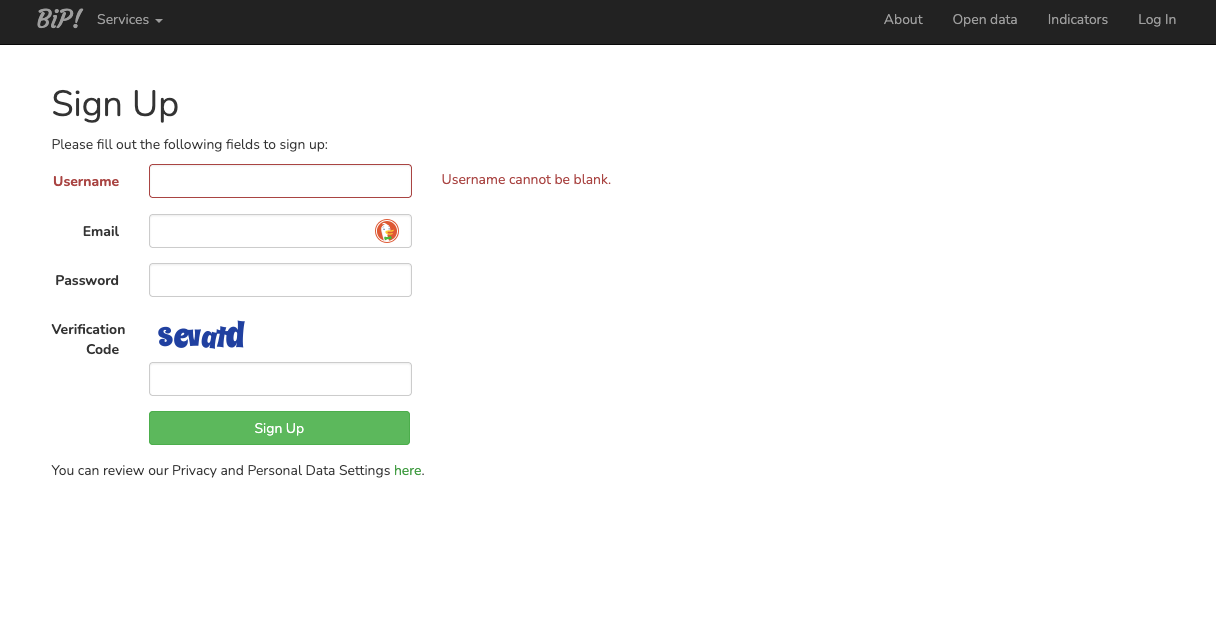
Congratulations! You have created a BIP! Services account!
BIP! Scholar
Create a BIP! Scholar academic profile
Go to the main BIP! Scholar page and click the "Create Profile" button.
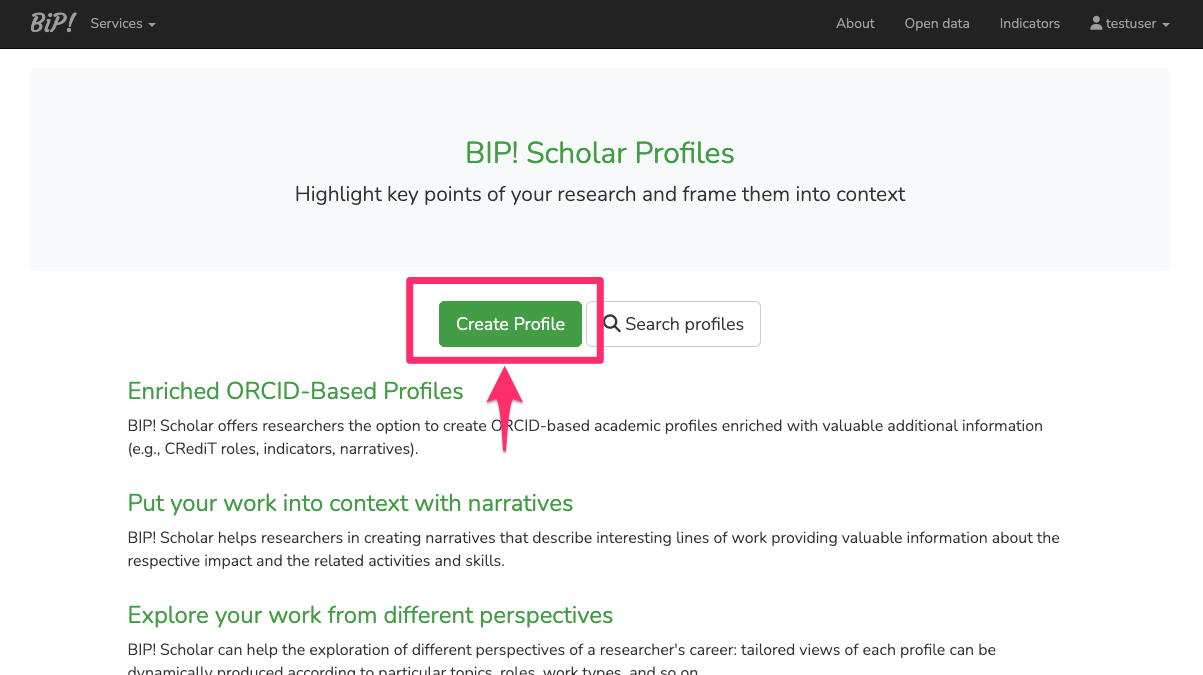
On the new page, click "Link with your ORCID" and follow the ORCID system's instructions to grant permission for syncing your ORCID account with your BIP! Scholar profile.
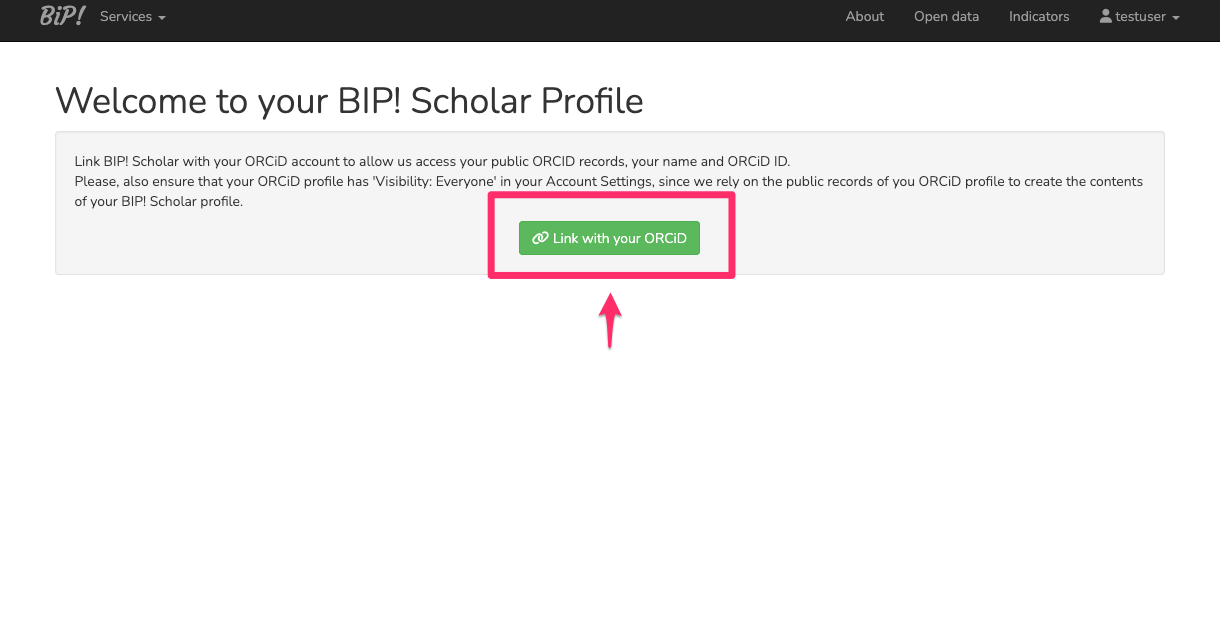
That's it! Your BIP! Scholar profile is now created and includes all public records from your ORCID profile. By default, all profiles remain private for self-monitoring unless you choose to make them public for sharing with everyone.
BIP! Finder
In a nutshell
BIP! Finder is an advanced academic search engine that allows literature exploration and scientific knowledge discovery. It is built upon the OpenAIRE Graph, a comprehensive knowledge base of scientific publications and research outputs.
Search
The environment offers advanced search functionalities for research products (publications, datasets, software, etc) within the domain of interest:
- End-users can use keywords to search for a topic of interest.
- Operators AND, OR, and NOT (written in capital letters): Can be used to combine the keywords according to the desired query semantics. Parentheses can be used to group together keywords combined with these operators.
- Space-separated keywords are considered all together by the system, applying an implicit AND operator.
- Double quotes can be used to search for appearances of the enclosed keywords as an exact phrase match.
- They can also refine the search results by applying various filters (e.g., impact indicator classes, type of research products).
- Finally, end-users can change the default ranking scheme for the results. An array of impact indicators (detailed here) combined with keyword relevance, are among the options. This can be useful for different use cases. For instance, a student drafting a survey on a topic should prioritise works with high influence, while an experienced researcher who revisits the same topic may prefer to find works with high popularity).
The search results appear as a list of rows. Each row displays valuable metadata for the respective research product including predetermined annotations from the connected knowledge base. A snapshot of the respective search interface, with the top results displayed, can be found below.
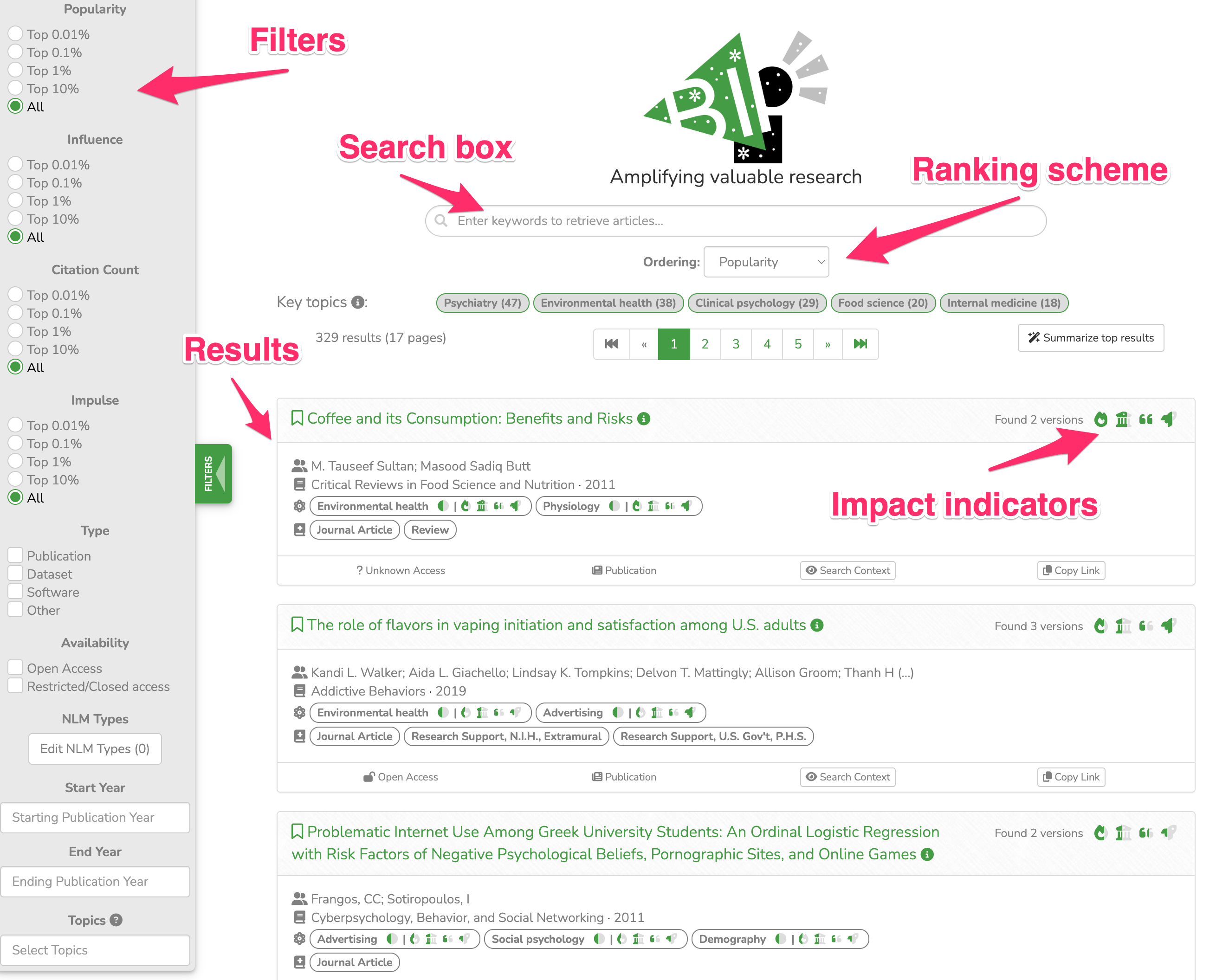
AI-generated summaries (for registered users).
Registered BIP! Finder end-users have also the option to ask for AI-generated summaries of the top search results. This can be done by clicking on the “Summarise top results” button placed at the top right corner of the search results section. The summaries are generated by a generative AI model that synthesizes the titles and abstracts from the top-k search results. By default, k is set to 5, but users can adjust this value to regenerate the summary based on a different number of results. Please note that a daily quota limits the number of summaries each user can produce, and a counter displays the remaining allowance.
This feature offers an interesting use case: comparing summaries generated using different ranking schemes. For example, a substantial difference in the narrative between summaries based on popularity versus influence, ranking could indicate a shift in the prevailing literature's focus over time.
BIP! Spaces
In a nutshell
Each BIP! Space is an academic search engine tailored for the needs of a specific organisation or community. More importantly, each space is connected with a knowledge base that encodes annotations related to the domain of interest determined by the organisation or community that owns it. A BIP! Space is created upon request (if you are interested, please send an email at bip@athenarc.gr).
Search
The environment offers advanced search functionalities for research products (publications, datasets, software, etc) within the domain of interest:
- End-users can use keywords to search for a topic of interest.
- Operators AND, OR, and NOT (written in capital letters) can be used to combine the keywords according to the desired query semantics. Parentheses can be used to group together keywords combined with these operators.
- Space-separated keywords are considered all together by the system, applying an implicit AND operator.
- Double quotes can be used to search for appearances of the enclosed keywords as an exact phrase match.
- They can also refine the search results by applying various filters (e.g., impact indicator classes, type of research products).
- Finally, end-users can change the default ranking scheme for the results. An array of impact indicators (detailed here) combined with keyword relevance, are among the options. This can be useful for different use cases. For instance, a student drafting a survey on a topic should prioritise works with high influence, while an experienced researcher who revisits the same topic may prefer to find works with high popularity).
The search results appear as a list of rows. Each row displays valuable metadata for the respective research product including predetermined annotations from the connected knowledge base. A snapshot of the respective search interface, with the top results displayed, can be found below.
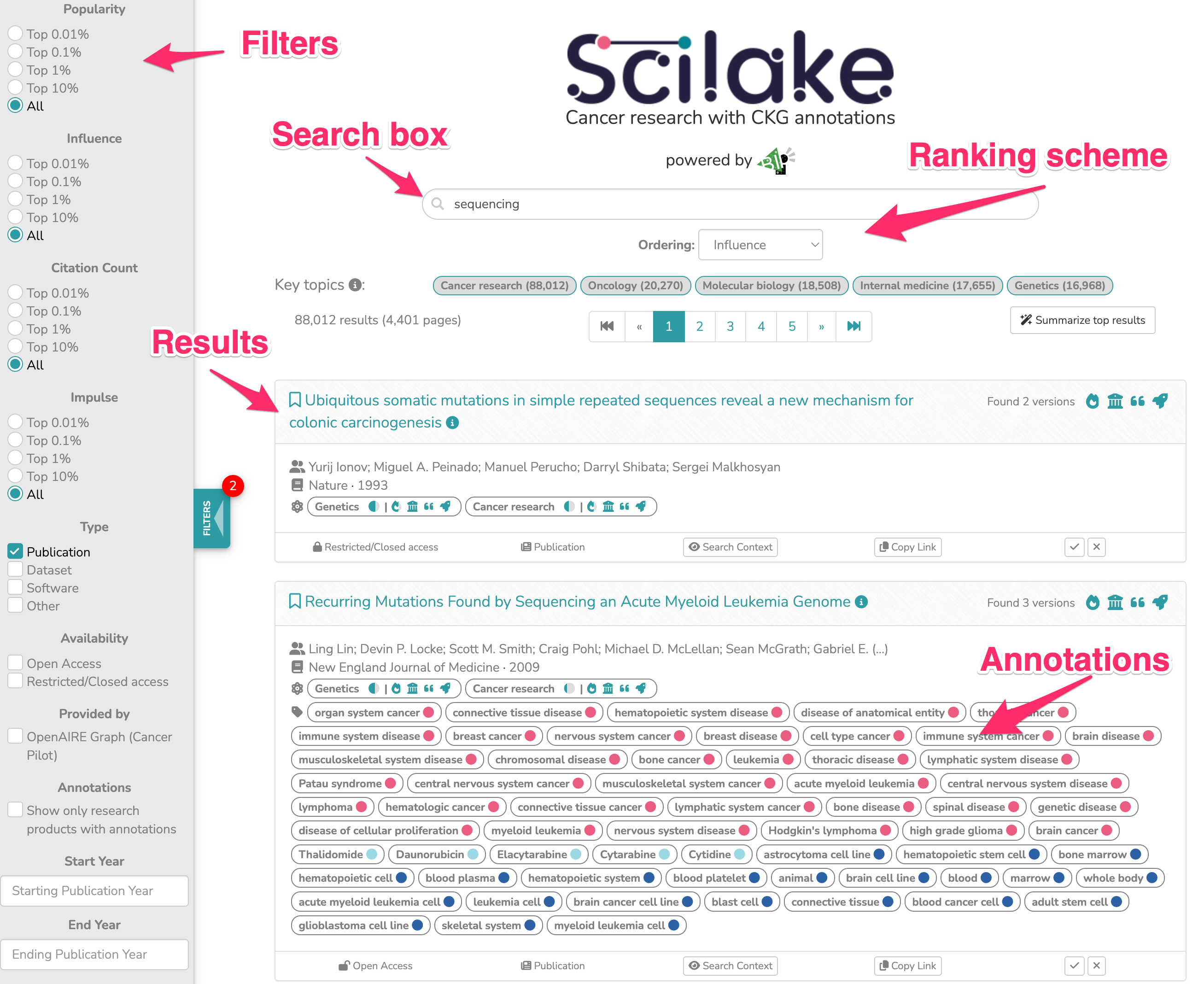
AI-generated summaries (for registered users)
Registered BIP! Space end-users have also the option to ask for AI-generated summaries of the top search results. This can be done by clicking on the “Summarise top results” button placed at the top right corner of the search results section. The summaries are generated by a generative AI model that synthesizes the titles and abstracts from the top-k search results. By default, k is set to 5, but users can adjust this value to regenerate the summary based on a different number of results. Please note that a daily quota limits the number of summaries each user can produce, and a counter displays the remaining allowance.
This feature offers an interesting use case: comparing summaries generated using different ranking schemes. For example, a substantial difference in the narrative between summaries based on popularity versus influence ranking could indicate a shift in the prevailing literature's focus over time.
Service feedback (for registered users, if enabled by the owner)
BIP! Space owners can enable the “Feedback Mode” to gather end-user input. This mode adds two distinct feedback mechanisms to the space:
- Result Evaluation: Users can assess the relevance or appropriateness of search results by clicking the “✓” (tick) or “x” (cross) icon next to an entry.
- Annotation Verification: Users confirm the correctness of an annotation by clicking “✓” or report an error by clicking “x”.
All feedback (“✓” or “x”) is immediately stored in the internal database upon clicking. Crucially, this feedback does not immediately alter the underlying database or knowledge base. Changes based on the collected feedback can be implemented later, upon request from the Space owner. If a feedback button was clicked accidentally, the user can click the same button again to cancel the submission.
Service configuration (for space owners)
Each space can be tailored according to the needs of the organisation or community that owns it. There are various customisation options related to:
- The styling of the space (e.g., logo, color schemes).
- The default search configuration (e.g., default ranking scheme and filters).
Apart from that, the space owner can determine the knowledge base to be used for the annotations, as well as the set of annotations to be displayed in the results. Currently, all these configurations are made by the BIP! Services support team after consultation with the space owner.